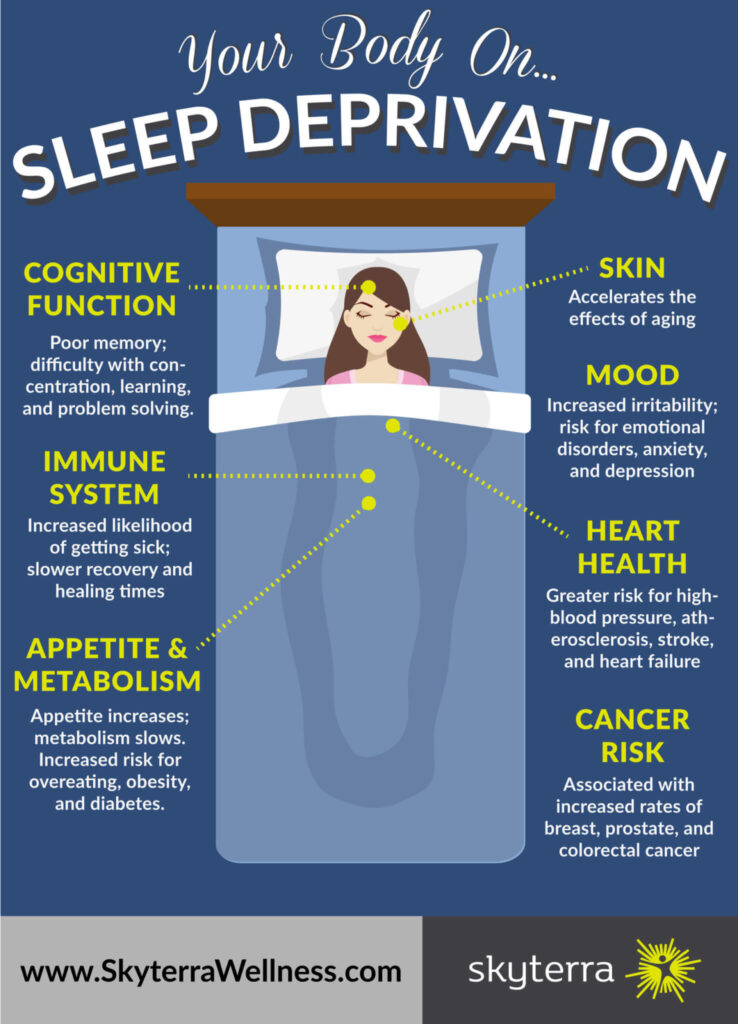
In recent years, the alarming connection between sleep deprivation and higher cancer rates has garnered significant attention from researchers and health professionals alike. Sleep deprivation, characterized by insufficient sleep duration or poor sleep quality, has been linked to various health issues, including an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer. As we delve into this critical topic, we will explore the underlying mechanisms that may explain this association and the implications for public health.
Throughout this article, you will discover how chronic sleep deprivation can disrupt hormonal balance, weaken the immune system, and lead to inflammation—all factors that may contribute to cancer development. We will also examine recent studies that highlight the correlation between sleep patterns and cancer incidence, shedding light on the importance of prioritizing sleep for overall health. By understanding these connections, you can take proactive steps to improve your sleep hygiene and potentially reduce your cancer risk.
As we navigate through the complexities of sleep and its impact on cancer rates, we encourage you to reflect on your own sleep habits and consider the changes you can make for a healthier lifestyle. Stay with us as we uncover valuable insights and practical tips that can help you achieve better sleep quality and enhance your well-being. Your health is worth the investment, and understanding the link between sleep deprivation and cancer could be a crucial step in safeguarding it.
Understanding Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation refers to the condition of not having enough sleep. It can be chronic or acute and is often caused by lifestyle choices, medical conditions, or environmental factors. Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to a range of health issues, including cognitive impairment, weakened immune function, and increased stress levels. The importance of sleep cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in physical health, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life.
Research has shown that sleep deprivation can disrupt the body’s natural circadian rhythms, which regulate various biological processes. This disruption can lead to hormonal imbalances and increased inflammation, both of which are linked to the development of cancer. Understanding the mechanisms behind sleep deprivation is essential for recognizing its potential impact on cancer risk.
Link Between Sleep and Cancer
Numerous studies have indicated a correlation between sleep deprivation and an increased risk of various types of cancer, including breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers. The exact mechanisms are still being explored, but it is believed that sleep deprivation may affect the body’s ability to repair DNA and regulate cell growth. This can lead to mutations and the proliferation of cancerous cells.
Additionally, sleep deprivation can lead to increased levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol, which may promote tumor growth. The relationship between sleep and cancer is complex, and ongoing research aims to clarify how sleep patterns influence cancer development and progression.
Impact of Circadian Rhythms on Cancer
Circadian rhythms are the body’s internal clock that regulates sleep-wake cycles and other physiological processes. Disruption of these rhythms, often caused by irregular sleep patterns or shift work, has been linked to an increased risk of cancer. Studies suggest that individuals who work night shifts or have irregular sleep schedules may have a higher incidence of certain cancers due to the misalignment of their circadian rhythms.
When the circadian clock is disrupted, it can lead to alterations in hormone levels, particularly melatonin, which has been shown to have anti-cancer properties. Understanding the role of circadian rhythms in cancer risk is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate these risks, such as promoting regular sleep patterns and minimizing exposure to artificial light at night.
Sleep Deprivation and Immune Function
The immune system plays a vital role in identifying and eliminating cancer cells. Sleep deprivation can significantly impair immune function, making the body less capable of fighting off cancerous cells. Research has shown that lack of sleep can reduce the production of cytokines, which are essential for immune response and inflammation regulation.
Furthermore, chronic sleep deprivation can lead to an increase in inflammatory markers, which are associated with cancer progression. By understanding the relationship between sleep and immune function, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their sleep quality and potentially reduce their cancer risk.
Preventive Measures and Recommendations
To mitigate the risks associated with sleep deprivation and its link to cancer, it is essential to adopt healthy sleep habits. Recommendations include establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a restful sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants such as caffeine and electronic devices before bedtime. Additionally, incorporating relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, can help improve sleep quality.
Public health initiatives should also focus on raising awareness about the importance of sleep and its impact on overall health. By promoting good sleep hygiene and addressing factors that contribute to sleep deprivation, we can potentially reduce the incidence of sleep-related health issues, including cancer.
Future Research Directions
As the link between sleep deprivation and cancer becomes increasingly recognized, future research will be crucial in understanding the underlying mechanisms and developing effective interventions. Studies focusing on the impact of sleep quality, duration, and circadian rhythm alignment on cancer risk will provide valuable insights.
Moreover, exploring the role of lifestyle factors, such as diet and physical activity, in conjunction with sleep patterns may help identify comprehensive strategies for cancer prevention. Continued research in this area will be essential for informing public health policies and improving individual health outcomes.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Sleep deprivation refers to the condition of not having enough sleep, which can be chronic or acute. |
| Research Findings | Studies have shown a correlation between sleep deprivation and an increased risk of various types of cancer, including breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers. |
| Mechanisms | Potential mechanisms include hormonal imbalances, weakened immune response, and increased inflammation due to lack of sleep. |
| Statistics | Research indicates that individuals who consistently get less than 6 hours of sleep per night may have a significantly higher risk of developing cancer. |
| Recommendations | To mitigate risks, it is recommended to prioritize sleep hygiene, aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. |
| Conclusion | Addressing sleep deprivation is crucial for overall health and may play a significant role in cancer prevention strategies. |