The Future of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) is a topic that has garnered significant attention in recent years. As governments and central banks around the world explore the potential of digital currencies, the landscape of finance is poised for a transformative shift. CBDCs represent a new era of monetary policy, offering a digital alternative to traditional cash and private cryptocurrencies. This article delves into the implications of CBDCs, their design, and the challenges they may face in the global economy.
In the following sections, we will explore the various types of CBDCs being considered by different countries, highlighting their unique features and potential benefits. You will learn about the technological advancements that enable these digital currencies, as well as the regulatory frameworks that are being developed to ensure their safe implementation. Additionally, we will discuss the potential impact of CBDCs on financial inclusion, payment systems, and the overall economy.
As we navigate through the complexities of CBDCs, we invite you to join us on this enlightening journey. By understanding the future of Central Bank Digital Currencies, you will gain valuable insights into how these innovations could reshape the way we conduct transactions, save money, and interact with our financial institutions. Stay with us as we uncover the exciting possibilities that lie ahead in the world of digital currencies.
1. Introduction to CBDCs
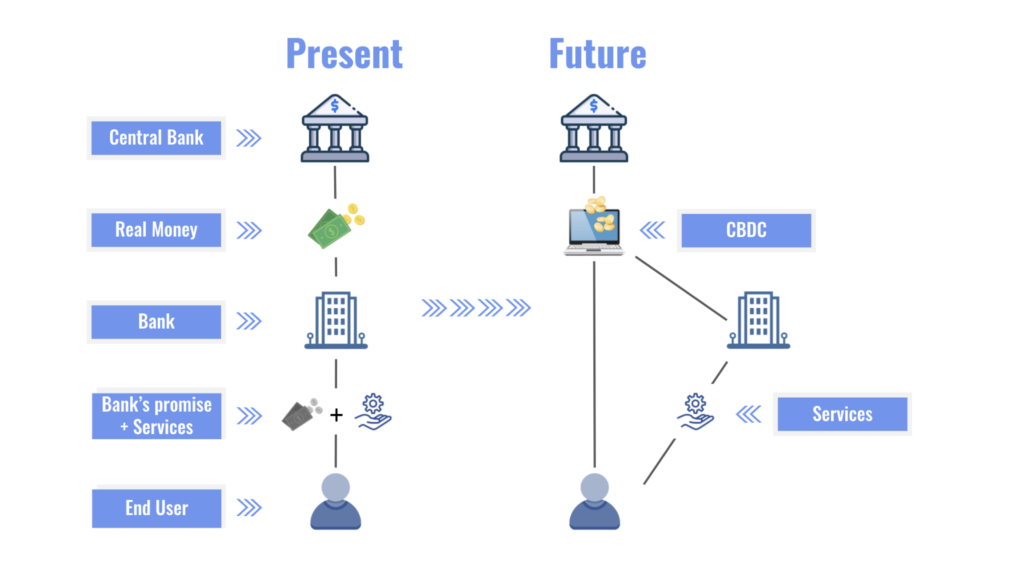
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) represent a significant evolution in the way money is conceptualized and utilized in the modern economy. Unlike cryptocurrencies, which are decentralized and often volatile, CBDCs are issued and regulated by central banks, providing a stable digital alternative to traditional fiat currencies. This introduction sets the stage for understanding the implications of CBDCs on monetary policy, financial stability, and the overall economy.
The rise of digital payment systems and the decline of cash usage have prompted central banks worldwide to explore the potential of CBDCs. As digital transactions become increasingly prevalent, the need for a secure, efficient, and universally accepted digital currency has never been more critical. This section will delve into the fundamental concepts of CBDCs and their potential impact on the financial landscape.
2. Benefits of CBDCs
One of the primary advantages of CBDCs is their ability to enhance financial inclusion. By providing a digital currency that can be accessed via smartphones and other devices, CBDCs can reach unbanked populations, allowing them to participate in the financial system. This can lead to increased economic activity and improved living standards for many individuals.
Additionally, CBDCs can streamline payment systems, reducing transaction costs and increasing the speed of cross-border payments. This efficiency can foster greater economic integration and facilitate international trade. Furthermore, CBDCs can enhance the effectiveness of monetary policy by providing central banks with real-time data on economic activity, enabling more informed decision-making.
3. Challenges and Risks of CBDCs
Despite their potential benefits, the implementation of CBDCs is not without challenges. One significant concern is the risk of disintermediation of commercial banks. If consumers prefer to hold CBDCs directly with the central bank, it could undermine the traditional banking system, leading to reduced lending capacity and financial instability.
Moreover, the introduction of CBDCs raises questions about privacy and security. Central banks must balance the need for transaction transparency with the protection of individual privacy. Cybersecurity threats also pose a significant risk, as digital currencies could become targets for hackers. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the successful deployment of CBDCs.
4. Global Trends in CBDC Development
Various countries are at different stages of CBDC development, with some already piloting their digital currencies. For instance, China’s digital yuan has gained significant attention, showcasing the potential for CBDCs to reshape the global financial landscape. Other countries, such as Sweden and the Bahamas, are also exploring or implementing their digital currencies.
This section will provide an overview of global trends in CBDC development, highlighting key initiatives and the motivations behind them. Understanding these trends can offer valuable insights into the future trajectory of CBDCs and their potential to influence international monetary systems.
5. CBDCs and Monetary Policy
CBDCs have the potential to transform the way monetary policy is conducted. By providing central banks with direct access to real-time data on economic transactions, CBDCs can enhance the effectiveness of monetary policy tools. For example, central banks could implement negative interest rates more effectively through CBDCs, encouraging spending and investment during economic downturns.
Furthermore, CBDCs could facilitate more targeted monetary policy measures, allowing central banks to influence specific sectors of the economy. This section will explore the implications of CBDCs for monetary policy and how they could reshape the relationship between central banks and the economy.
6. The Role of CBDCs in Financial Stability
Financial stability is a critical concern for central banks, and CBDCs could play a pivotal role in enhancing it. By providing a secure and stable digital currency, CBDCs can reduce the risks associated with bank runs and enhance the resilience of the financial system. In times of crisis, individuals may prefer to hold CBDCs over traditional bank deposits, providing a safe haven for their assets.
This section will examine the potential of CBDCs to contribute to financial stability, discussing how they can mitigate risks and enhance the overall robustness of the financial system. Additionally, it will address the challenges that may arise in maintaining stability in a digital currency environment.
7. CBDCs and the Future of Payments
The introduction of CBDCs is poised to revolutionize the payments landscape. With the rise of digital wallets and contactless payments, CBDCs can offer a seamless and efficient payment experience for consumers and businesses alike. This shift could lead to a decline in cash usage and a transformation of the retail payment ecosystem.
Moreover, CBDCs can facilitate cross-border transactions, reducing the costs and time associated with international payments. This section will explore the future of payments in a CBDC-dominated world, highlighting the potential for innovation and efficiency in the payments industry.
8. Conclusion: The Path Forward for CBDCs
As central banks continue to explore the potential of CBDCs, the path forward will require careful consideration of the benefits and challenges associated with digital currencies. Collaboration between central banks, governments, and the private sector will be essential to ensure the successful implementation of CBDCs.
In conclusion, the future of CBDCs holds great promise, but it also presents significant challenges that must be addressed. By navigating these complexities, central banks can harness the potential of CBDCs to create a more inclusive, efficient, and stable financial system for the future.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are digital forms of a country’s fiat currency issued and regulated by the central bank. As the world moves towards a more digital economy, CBDCs are gaining traction as a potential solution to various financial challenges. This article explores the future of CBDCs, their benefits, challenges, and implications for the global financial system.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A digital currency issued by a central bank, representing a digital form of fiat money. |
| Benefits |
|
| Challenges |
|
| Global Trends | Many countries are exploring or piloting CBDCs, including China, the European Union, and the United States. |
| Future Implications |
|
Conclusion
The future of Central Bank Digital Currencies holds significant promise for enhancing the efficiency and inclusivity of financial systems worldwide. However, careful consideration of the associated challenges and risks is essential to ensure that CBDCs serve the public interest and contribute to a stable financial environment.