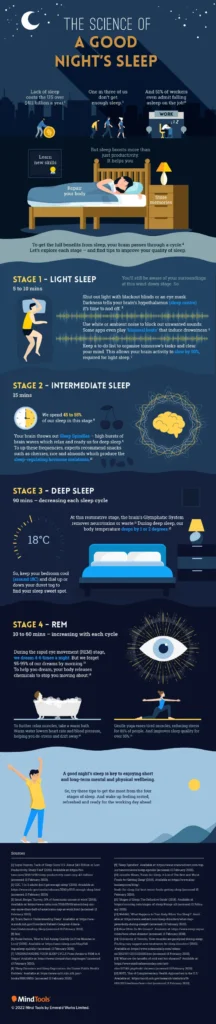
A good night’s sleep is essential for overall health and well-being. **The Science Behind A Good Night’s Sleep** has been a topic of interest for researchers and scientists for many years. It is well-known that sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation, cognitive function, and emotional regulation. Additionally, **the science behind a good night’s sleep** also involves the body’s natural circadian rhythm and the release of hormones such as melatonin, which help regulate the sleep-wake cycle. Furthermore, the quality of sleep is influenced by factors such as environmental conditions, stress levels, and lifestyle choices.
One of the most intriguing aspects of **The Science Behind A Good Night’s Sleep** is the impact of technology on sleep patterns. The use of electronic devices before bedtime can disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, leading to difficulties in falling asleep and reduced overall sleep quality. Additionally, the relationship between diet and sleep quality is an interesting area of study within **the science behind a good night’s sleep**. Certain foods and drinks can either promote or hinder a restful night’s sleep, making nutrition an important factor to consider for those seeking to improve their sleep habits. Understanding the various factors that contribute to a good night’s sleep is essential for promoting overall well-being and productivity.
The Science Behind A Good Night’s Sleep
Understanding the science behind a good night’s sleep can help us appreciate the importance of quality rest for our overall health and well-being. Sleep is a complex process that involves different stages, including non-rapid eye movement (NREM) and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. During NREM sleep, the body repairs tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens the immune system. REM sleep, on the other hand, is essential for cognitive function, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation. These stages work together to ensure that we wake up feeling refreshed and rejuvenated.
Furthermore, the body’s internal clock, known as the circadian rhythm, plays a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. This biological process is influenced by external factors such as light and temperature, and it helps determine the times when we feel most alert and when we naturally feel sleepy. Understanding the science behind the circadian rhythm can help us establish healthy sleep habits and improve the quality of our rest.
| Factor | Impact | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Light | Decreases melatonin production | Exposure to light, especially blue light from screens, can disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. |
| Temperature | Affects sleep quality | Both too hot and too cold temperatures can interfere with the body’s ability to fall and stay asleep. |
| Stress | Increases cortisol levels | Elevated stress levels can lead to increased production of cortisol, a hormone that can interfere with sleep. |
| Diet | Impacts sleep patterns | Consuming caffeine, heavy meals, or alcohol close to bedtime can disrupt the body’s ability to fall asleep and stay asleep. |
| Exercise | Promotes better sleep | Regular physical activity can help regulate sleep patterns and improve sleep quality. |
SONUÇ
The Science Behind A Good Night’s Sleep konusunda, ışık, sıcaklık, stres, diyet ve egzersizin uyku kalitesi üzerindeki etkileri göz önüne alındığında, bu faktörlerin uyku düzenini ve kalitesini nasıl etkilediği konusunda bilimsel bir açıklama yapılmıştır. Bu faktörlerin dengelenmesi, iyi bir gece uykusu için önemlidir.